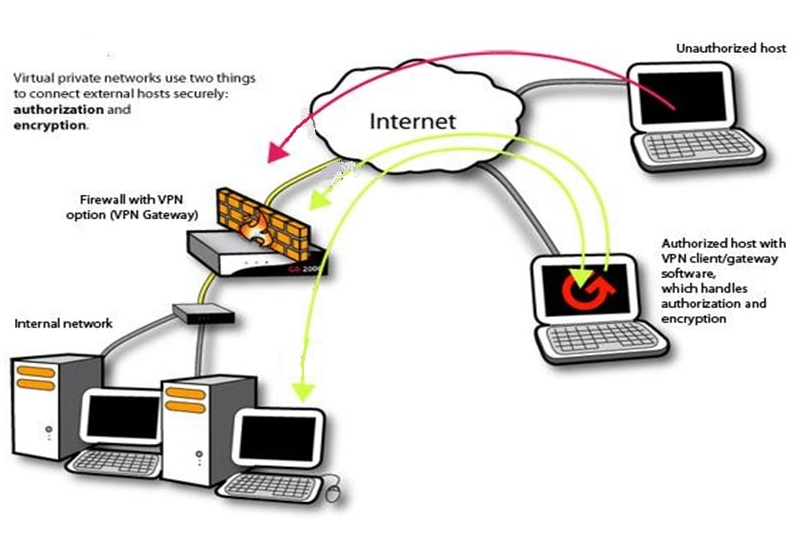
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a technology that allows you to establish a secure and encrypted connection between your device and the internet. It creates a private network connection over a public network, such as the internet, enabling you to access the internet securely and privately.
When you connect to a VPN server, all your internet traffic is routed through an encrypted tunnel, which protects your data from being intercepted or monitored by hackers, government agencies, or other third parties. It effectively hides your IP address and encrypts your online activities, providing you with privacy and anonymity.
There are several benefits of using a VPN:
- Security: A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it extremely difficult for anyone to intercept and decipher your data. This is especially useful when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, which are often insecure and prone to hacking.
- Privacy: By masking your IP address and encrypting your online activities, a VPN shields your identity and browsing history from your internet service provider (ISP), advertisers, and other entities that may track your online behavior.
- Anonymity: When you connect to a VPN server, your real IP address is replaced with the IP address of the server, making it harder for websites, services, or other online entities to track your location or identify you.
- Bypassing Geographical Restrictions: A VPN can allow you to bypass geographical restrictions imposed by certain websites or streaming services. By connecting to a VPN server in a different country, you can appear as if you’re accessing the internet from that location, giving you access to content that may be blocked in your region.
- Remote Access: VPNs are commonly used by businesses to provide secure remote access to their employees. This allows employees to connect to their company’s network from outside the office, ensuring their data and communications remain protected.
It’s important to note that while VPNs provide increased privacy and security, they don’t make you completely anonymous online. VPN providers can potentially log your activities, and if compelled by law enforcement or government agencies, they may be required to hand over that information. Therefore, it’s essential to choose a reputable VPN provider that has a strong privacy policy and doesn’t keep logs of user activity.
VPN history
The history of VPNs dates back to the late 20th century when organizations and researchers began developing ways to establish secure remote connections. Here’s a brief overview of the history of VPNs:
- Early Development (1990s): The groundwork for VPN technology was laid in the 1990s. Cryptographer Whitfield Diffie and his colleagues introduced the concept of public-key cryptography, which formed the basis for secure communication over the internet. The development of encryption protocols, such as Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), provided the framework for creating secure virtual private networks.
- PPTP and Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP): In the late 1990s, Microsoft developed PPTP, a protocol that allowed secure remote access to corporate networks. PPTP quickly became popular due to its simplicity and compatibility with Windows operating systems. L2TP, introduced in collaboration with Cisco, merged PPTP with Cisco’s Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F) protocol to create a more secure and flexible VPN protocol.
- IPsec and SSL/TLS VPNs: In the early 2000s, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) developed IPsec (Internet Protocol Security), a suite of protocols that provided a secure framework for VPNs. IPsec became widely used for site-to-site VPN connections and was integrated into various network devices. Additionally, SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) VPNs gained popularity, allowing remote users to securely access web-based applications using standard web browsers.
- Advancements and Commercialization: Over time, VPN technology advanced, and commercial VPN services started emerging. These services offered individuals and businesses the ability to secure their internet connections and protect their privacy. OpenVPN, an open-source VPN protocol, gained popularity due to its flexibility and strong security features.
- Rise in Popularity: With growing concerns about online privacy, censorship, and cybersecurity threats, VPN usage increased significantly in the late 2000s and early 2010s. People started using VPNs to bypass geo-restrictions, access streaming services, protect their data on public Wi-Fi networks, and maintain anonymity online.
- Mobile VPNs and VPN Apps: As smartphones became ubiquitous, VPN providers developed mobile apps, allowing users to secure their internet connections on their mobile devices. This made VPNs more accessible and convenient for a broader range of users.
Today, VPNs continue to play a crucial role in ensuring online privacy and security. They have become an essential tool for individuals, businesses, and organizations, offering a secure and private way to access the internet and protect sensitive information.